Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Inoue, Tomio*; Hayakawa, Kazushige*; Shiotari, Harutaka*; Nakamura, Yoshihide*; Matsuyama, Kazuya*; Nagasawa, Kiyoshi*
no journal, ,
For Japan, application of radiation in nuclear medicine is prominently used for the diagnosis, the radiotherapy and the examination by radioisotopes (RI). They addressed to FDG-PET, charged particle therapy and BNCT at the specified hospitals. Incomes are reimbursed by a national health insurance. In 2005, reimbursed incomes at those hospitals were studied as an economic scale as a commissioned work from the Cabinet Office, Government of Japan. Results were directly compared with those from previous work done in 1997. The economic scale of the application of radiation to all medical reimbursement in our country is 14 billion dollars, which is larger by a factor of 17% than that of 1997. The value corresponds to about 4.8% of the national health expenditure (301billion dollars), consisting of 4.4% for medicine and 0.4% for dentistry.
 subunit in
subunit in 
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Ikeda, Daisuke*; Yanase, Sumino*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Ishii, Naoaki*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
Well-fed adult animals were exposed to cobalt-60  -rays, followed by the chemotaxis assay. A decrease in chemotaxis toward NaCl occurred only after combined starvation and exposure to NaCl. Irradiation led to an additional decrease in chemotaxis immediately after an acute dose in the transition stage of salt chemotaxis learning. Strikingly, chronic irradiation induced negative chemotaxis in the exposed animals, i.e., the primary avoidance response. Radiation-induced additional decreases in chemotaxis following acute and chronic irradiations were significantly suppressed in the
-rays, followed by the chemotaxis assay. A decrease in chemotaxis toward NaCl occurred only after combined starvation and exposure to NaCl. Irradiation led to an additional decrease in chemotaxis immediately after an acute dose in the transition stage of salt chemotaxis learning. Strikingly, chronic irradiation induced negative chemotaxis in the exposed animals, i.e., the primary avoidance response. Radiation-induced additional decreases in chemotaxis following acute and chronic irradiations were significantly suppressed in the 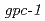 mutant, which was defective in GPC-1 (one of the two
mutant, which was defective in GPC-1 (one of the two  subunits of the heterotrimeric G protein). The data suggest that radiation behaves as a modulator in salt chemotaxis learning via
subunits of the heterotrimeric G protein). The data suggest that radiation behaves as a modulator in salt chemotaxis learning via  GPC-1 and a specific neuronal network, and may shed light on the modulatory effect of radiation on learning.
GPC-1 and a specific neuronal network, and may shed light on the modulatory effect of radiation on learning.
Saito, Kimiaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English